What is the most cost-effective core material for high-volume production?
For high-volume production, silicon steel (0.20-0.35mm) remains the most cost-effective option. It offers an excellent balance of performance, manufacturability, and cost. For applications requiring better high-frequency performance, ultra-thin silicon steel (0.10-0.15mm) provides improved efficiency with only a moderate cost increase. Advanced composite laminations can also reduce total manufacturing cost through simplified assembly processes.
How do I choose between amorphous metals and nanocrystalline cores?
The choice depends on your specific requirements: Amorphous metals offer the lowest core losses (70-90% lower than silicon steel) and are ideal for applications where efficiency is paramount. Nanocrystalline cores provide a better combination of high permeability and low losses, along with superior temperature stability and mechanical properties. Generally, choose amorphous metals for maximum efficiency at high frequencies, and nanocrystalline cores when you need balanced performance across a wider range of operating conditions.
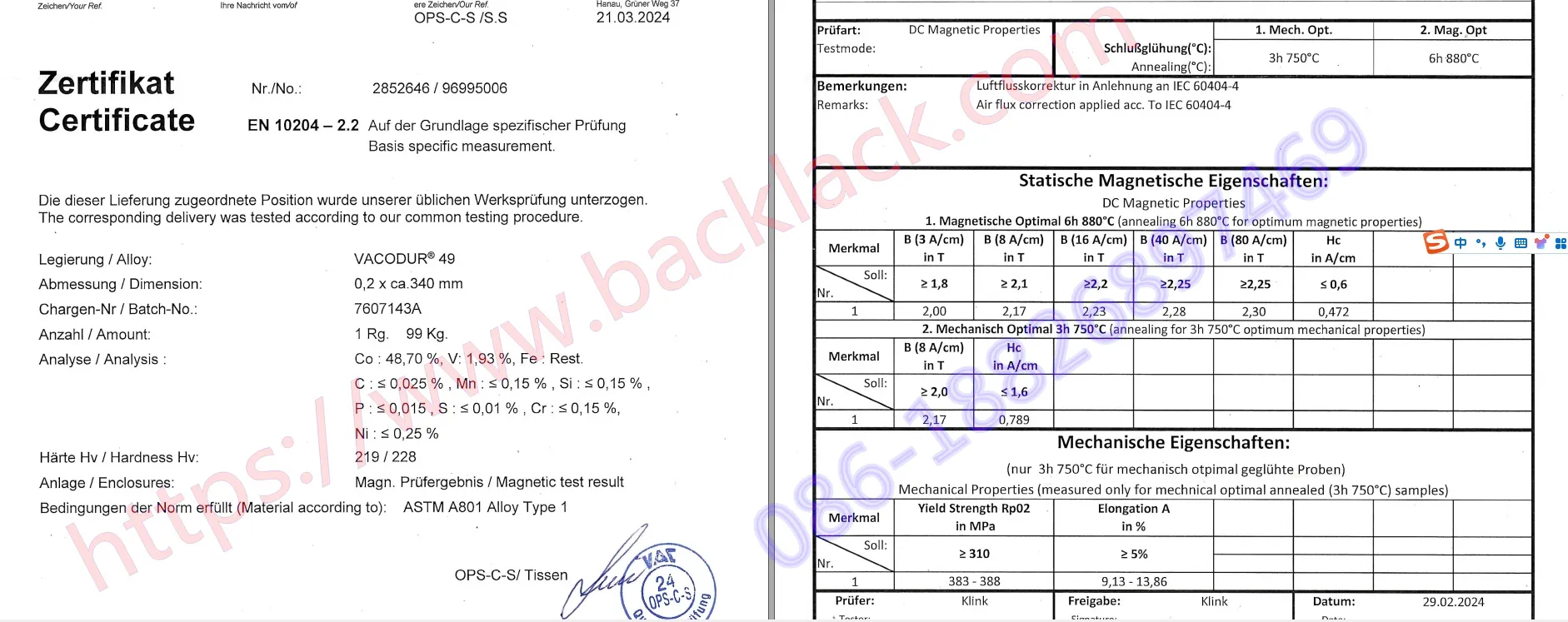
Are cobalt-iron alloys worth the premium cost for EV applications?
For premium EV applications where power density and efficiency are critical, cobalt-iron alloys like Vacodur 49 can provide significant advantages. The 2-3% efficiency gain and 20-30% size reduction can justify the higher material cost in performance-oriented vehicles. However, for mass-market EVs, advanced silicon steel grades often provide better overall value. We recommend conducting a total lifecycle cost analysis including efficiency gains, battery size reduction potential, and thermal management savings.
What manufacturing considerations are different for advanced core materials?
Advanced materials often require specialized manufacturing approaches: Laser cutting instead of stamping to prevent stress-induced magnetic degradation, specific heat treatment protocols with controlled atmospheres, compatible insulation systems that withstand higher temperatures, and modified stacking/bonding techniques. It's essential to involve material suppliers early in the design process to optimize both material selection and manufacturing approach.
What thicknesses are there for motor lamination steel? 0.1MM?
The thickness of motor core lamination steel grades includes 0.05/0.10/0.15/0.20/0.25/0.35/0.5MM and so on. From large steel mills in Japan and China. There are ordinary silicon steel and 0.065 high silicon silicon steel. There are low iron loss and high magnetic permeability silicon steel. The stock grades are rich and everything is available..
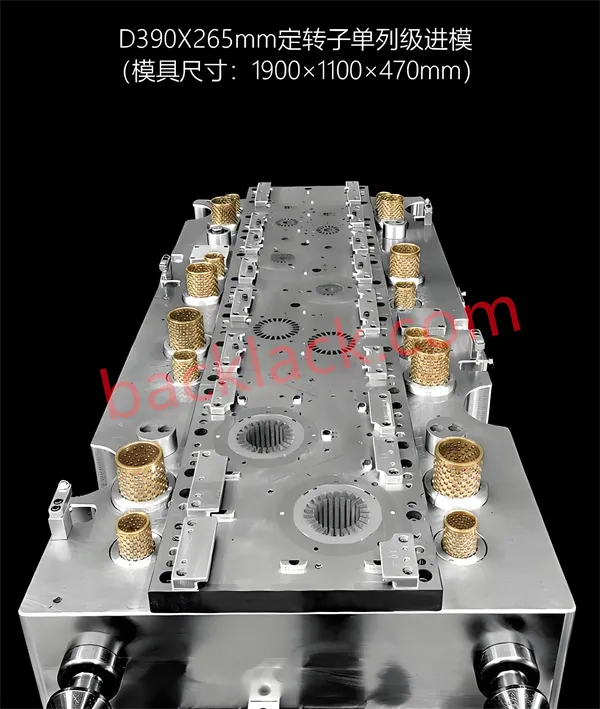
What manufacturing processes are currently used for motor lamination cores?
In addition to stamping and laser cutting, wire etching, roll forming, powder metallurgy and other processes can also be used. The secondary processes of motor laminations include glue lamination, electrophoresis, insulation coating, winding, annealing, etc.
How to order motor laminations?
You can send us your information, such as design drawings, material grades, etc., by email. We can make orders for our motor cores no matter how big or small, even if it is 1 piece.
How long does it usually take you to deliver the core laminations?
Our motor laminate lead times vary based on a number of factors, including order size and complexity. Typically, our laminate prototype lead times are 7-20 days. Volume production times for rotor and stator core stacks are 6 to 8 weeks or longer.
Can you design a motor laminate stack for us?
Yes, we offer OEM and ODM services. We have extensive experience in understanding motor core development.
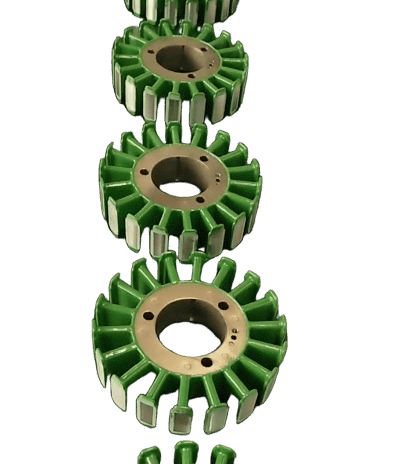
What is the advantages of bonding vs welding on rotor and stator?
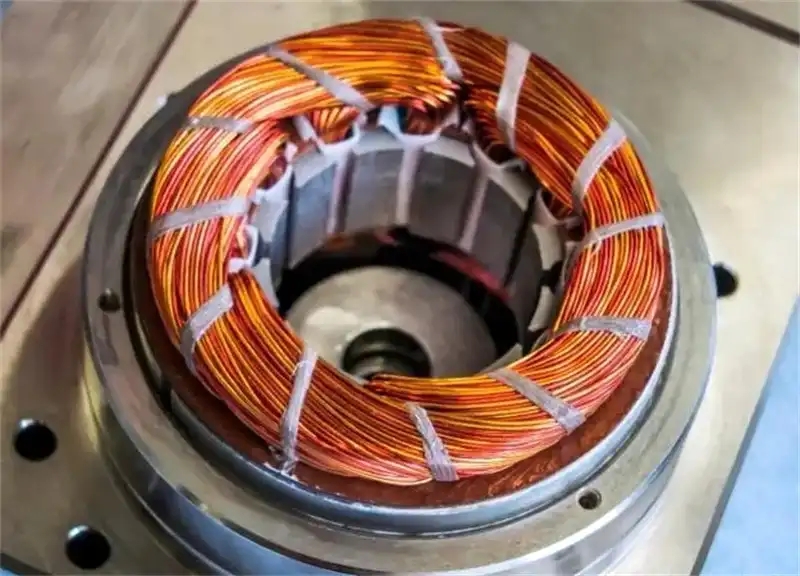
The concept of rotor stator bonding means using a roll coat process that applies an insulating adhesive bonding agent to the motor lamination sheets after punching or laser cutting. The laminations are then put into a stacking fixture under pressure and heated a second time to complete the cure cycle. Bonding eliminates the need for a rivet joints or welding of the magnetic cores, which in turn reduces interlaminar loss. The bonded cores show optimal thermal conductivity, no hum noise, and do not breathe at temperature changes.
Can glue bonding withstand high temperatures?
Absolutely. The glue bonding technology we use is designed to withstand high temperatures. The adhesives we use are heat resistant and maintain bond integrity even in extreme temperature conditions, which makes them ideal for high-performance motor applications.
What is glue dot bonding technology and how does it work?
Glue dot bonding involves applying small dots of glue to the laminates, which are then bonded together under pressure and heat. This method provides a precise and uniform bond, ensuring optimal motor performance.
What is the difference between self-bonding and traditional bonding?
Self-bonding refers to the integration of the bonding material into the laminate itself, allowing the bonding to occur naturally during the manufacturing process without the need for additional adhesives. This allows for a seamless and long-lasting bond.
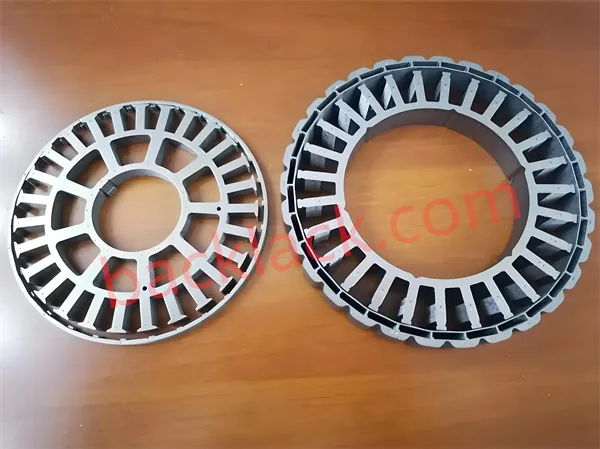
Can bonded laminates be used for segmented stators in electric motors?
Yes, bonded laminations can be used for segmented stators, with precise bonding between the segments to create a unified stator assembly. We have mature experience in this area. Welcome to contact our customer servic.