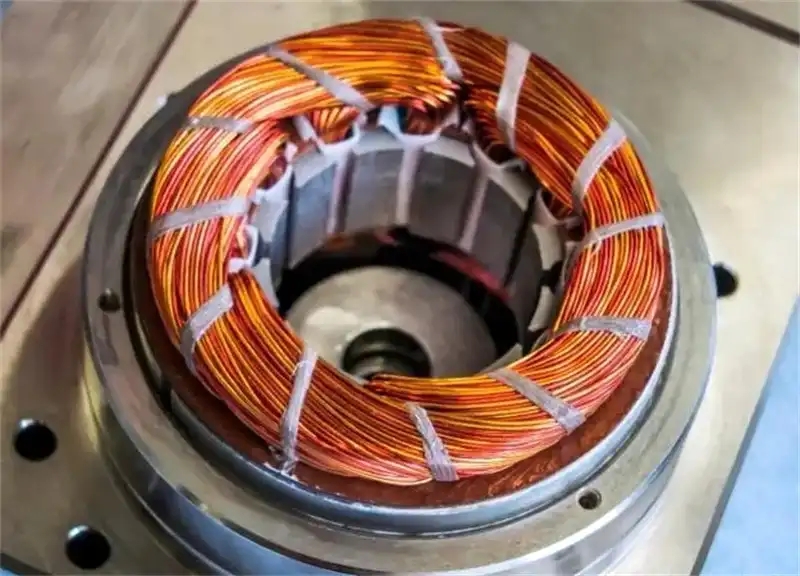
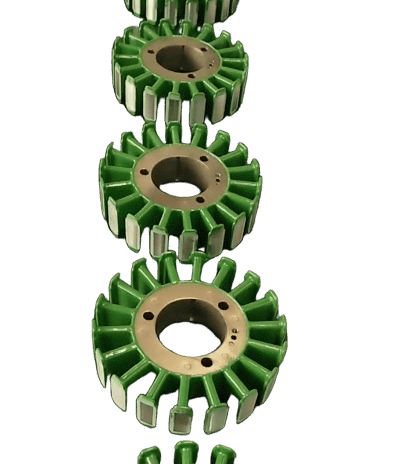
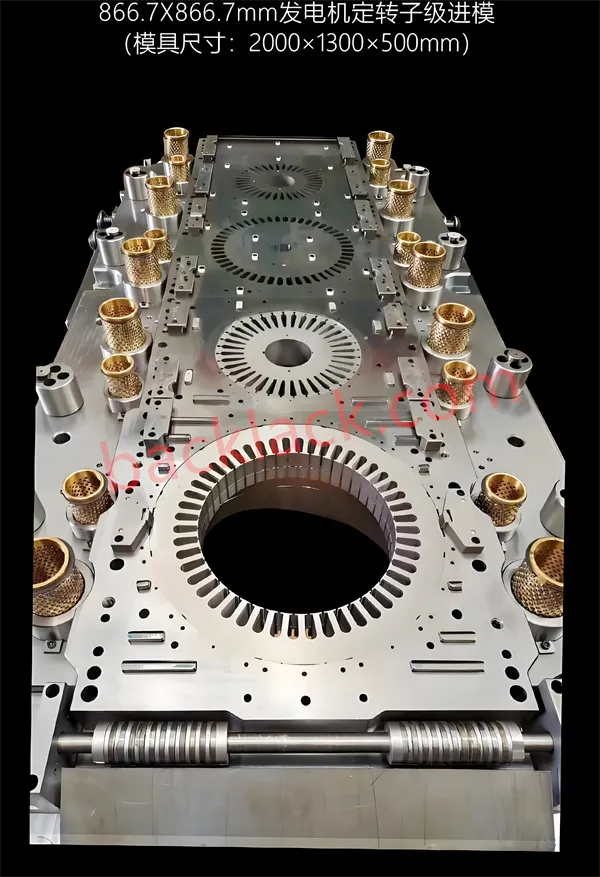
1. Avoid Common Pitfalls: Key Misconceptions in Stator Core Selection
In our daily processing, we’ve encountered numerous quality issues caused by improper manufacturer selection. Many buyers focus only on surface indicators, ignoring hidden risks. Here’s a summary of common misconceptions and their consequences, based on our practical cases:
| Common Misconception | Actual Risk (From Our Processing Experience) | Correct Evaluation Method | Hot Keywords |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prioritizing price over material grade | Using low-grade silicon steel (e.g., non-electrical steel) leads to 15-20% higher iron loss, causing motor overheating and shortened lifespan. We once processed cores that failed IE4 efficiency standards due to this issue. | Verify silicon steel grade certificates (e.g., 35WW270, 20WW1200) and test magnetic permeability (≥1.5T) with professional instruments. | electrical steel stator core, low iron loss silicon steel |
| Ignoring lamination gap uniformity | Uneven gaps (>0.05mm) increase magnetic resistance, leading to motor vibration and 8-12% lower efficiency. We had to rework 500+ cores due to poor lamination alignment. | Check lamination flatness with a laser interferometer and verify stacking pressure control records (2.0-3.5 MN/m²). | stator core lamination gap, precision lamination stacking |
| Overlooking post-processing deburring | Burrs (>0.03mm) scratch insulation layers, causing eddy current leakage and short circuits. This accounted for 30% of motor failure cases we handled. | Inspect core edges with a digital microscope and confirm deburring processes (mechanical grinding + ultrasonic cleaning). | stator core deburring, eddy current loss reduction |
| Blindly trusting batch test reports | Some manufacturers provide fake reports; we found 10% of sampled cores failed dimensional tolerance (inner diameter error >0.05mm) despite qualified reports. | Conduct random on-site sampling and test with a coordinate measuring machine (CMM) for key dimensions. | precision stamped stator core, stator core dimensional tolerance |
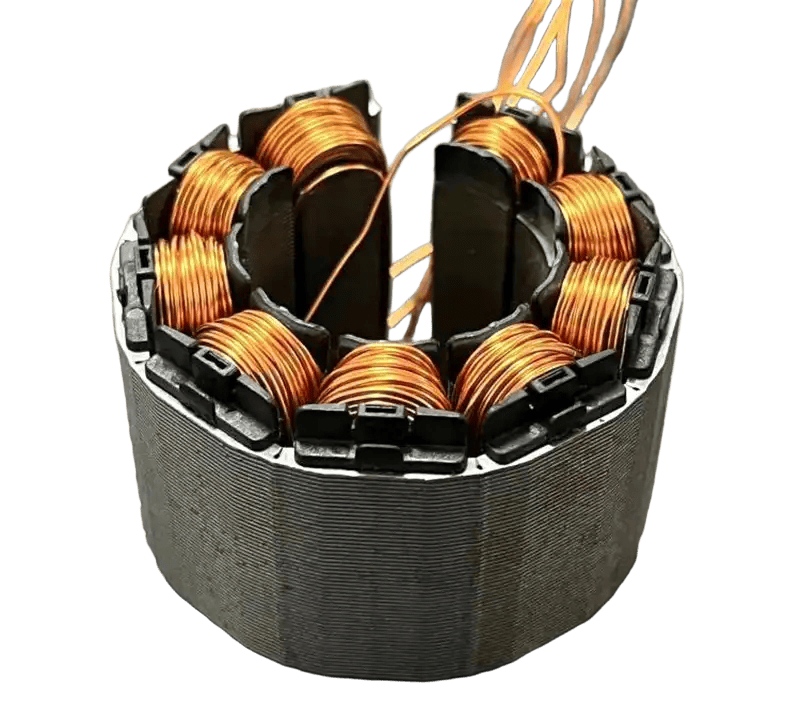
2. Core Evaluation Criteria: From Material to Process, Layer-by-Layer Screening
As a processing factory, we judge manufacturers by their ability to control "micro-precision"—details that are easily overlooked but critical to performance. Focus on the following four dimensions:
2.1 Material Sourcing & Processing: The Root of Performance
High-performance stator cores start with high-quality raw materials and professional processing. We prioritize manufacturers with strict material control:
| silicon steel Grade | Thickness Range | Key Performance | Suitable Motor Types | Hot Keywords |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B20AV1200-Z | 0.15-0.20mm | Ultra-low iron loss (≤1.2W/kg), high magnetic permeability | EV drive motors, high-end servo motors | ultra-low loss silicon steel, EV stator core material |
| B25AV1200-Z | 0.20-0.25mm | Low iron loss (≤1.3W/kg), balanced rigidity | Industrial servo motors, precision control motors | servo motor silicon steel, high permeability silicon steel |
| B35A250/35JNE250 | 0.30-0.35mm | Cost-effective, stable magnetic properties | Household appliance motors, general industrial motors | appliance silicon steel, cost-effective electrical steel |
| 50WW600 | 0.45-0.50mm | High mechanical strength, mass-production friendly | Low-power industrial pumps, fans | industrial motor silicon steel, mass-produced stator core material |
- Silicon Steel Grade Customization: For high-efficiency motors, low-loss silicon steel (e.g., 25WW1300 for EV motors) is essential. A top manufacturer will not only supply standard grades but also customize material thickness (0.15-0.5mm) based on your motor’s power density requirements. We once partnered with a manufacturer to use 0.2mm thin-gauge silicon steel, reducing iron loss by 18% for a client’s servo motor.
- Insulation Layer Treatment: The insulation layer must withstand high temperatures (up to 180°C for industrial motors) and mechanical stress. Reject manufacturers using solvent-based coatings—opt for water-based electrostatic coatings or ceramic insulation films, which offer better adhesion and heat resistance. We test insulation resistance (≥200MΩ at 500V DC) to ensure quality.
2.2 Stamping & Forming: Precision That Shapes Magnetic Circuits
Stamping accuracy directly determines the integrity of the stator core’s magnetic circuit. We pay close attention to different stamping processes and their applicability, summarized as follows:
| Stamping Process | Precision Range | Production Efficiency | Applicable Batch | Key Advantages/Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Progressive Die Stamping | ±0.02-±0.05mm | High (≥500 pieces/hour) | Mass production (≥10,000 pieces) | Advantage: Stable consistency; Disadvantage: High mold development cost |
| Laser Cutting Stamping | ±0.01-±0.03mm | Medium (100-300 pieces/hour) | Small-batch, custom parts | Advantage: High precision for complex shapes; Disadvantage: High unit cost |
| Compound Die Stamping | ±0.03-±0.08mm | Medium-high (300-400 pieces/hour) | Medium batch (1,000-10,000 pieces) | Advantage: Balanced cost and precision; Disadvantage: Limited shape complexity |
| Fine Blanking Stamping | ±0.015-±0.04mm | Low (50-150 pieces/hour) | High-end precision cores | Advantage: Smooth edge, no burr; Disadvantage: Slow efficiency |
- Die Technology & Maintenance: Progressive dies with hard chrome plating (HRC 62+) ensure stable precision stamping (±0.02mm) for mass production. Ask manufacturers for die maintenance logs—poorly maintained dies lead to dimensional drift and burrs. We once found a manufacturer’s dies had excessive wear, causing slot width error of 0.1mm.
- Forming Process Adaptability: For complex stator core structures (e.g., segmented stator cores for EVs), manufacturers need advanced forming technologies like laser cutting + bending. Verify their ability to process special slot shapes (e.g., fractional-slot concentrated windings) without compromising precision.
2.3 Quality Control: Full-Process Monitoring Instead of Final Inspection
High-performance stator cores require 100% process control, not just sampling inspection. We require manufacturers to have full-process QC, with key inspection items detailed below:
| QC Stage | Key Inspection Items | Acceptance Standard | Testing Tool | Google Hot Keywords |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incoming Material (IQC) | silicon steel composition, insulation thickness, magnetic permeability | Silicon content 3.0-3.5%, insulation thickness 0.01-0.03mm | Spectrometer, thickness gauge, magnetic tester | silicon steel inspection, stator core material QC |
| Stamping (IPQC) | Slot width, inner/outer diameter, burr size | Burr ≤0.03mm, dimensional tolerance ±0.02mm | Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM), digital microscope | stator core dimensional tolerance, precision stamping QC |
| Lamination (IPQC) | Stacking density, lamination gap, flatness | Gap ≤0.05mm, flatness ≤0.02mm/m | Laser interferometer, density meter | stator core lamination QC, lamination gap inspection |
| Final (FQC) | Insulation resistance, magnetic flux density, dynamic balance | Insulation resistance ≥200MΩ, dynamic balance ≤0.05g·cm | Megohmmeter, fluxmeter, dynamic balance tester | stator core quality control, insulation resistance test |
- Incoming Material Inspection (IQC): Strict testing of silicon steel’s chemical composition (silicon content 3.0-3.5%), magnetic properties, and insulation performance, with traceable batch records. Avoid manufacturers that skip IQC to cut costs.
- In-Process Inspection (IPQC): Real-time monitoring of stamping dimensional accuracy, lamination alignment, and coating thickness. We prefer manufacturers with automated inspection systems (e.g., machine vision) that can detect defects in 0.5 seconds per piece.
- Final Inspection (FQC): Comprehensive testing including core resistance, magnetic flux density, dynamic balance, and temperature cycle resistance. For EV stator cores, additional salt spray tests (48 hours) are required to ensure corrosion resistance.
2.4 Supply Chain & Technical Support: Long-Term Cooperation Guarantee
Beyond manufacturing capabilities, a manufacturer’s service and supply chain resilience are crucial for long-term cooperation:
- Customization Capability: As motor designs upgrade, custom stator cores are increasingly needed. A good manufacturer will assign a dedicated technical team to optimize designs—for example, we collaborated with a partner to adjust the stator core’s tooth shape, improving magnetic flux density by 12%.
- Delivery & Backup Capacity: Delays in stator core delivery disrupt production schedules. Verify the manufacturer’s monthly output (≥100,000 pieces for mass production) and raw material inventory (≥30 days of supply). Ask about backup production lines for emergency orders.
- After-Sales Service: Choose manufacturers that provide technical support for installation and debugging. We once worked with a manufacturer that sent engineers to our factory to solve core assembly issues, saving us 2 weeks of rework time.
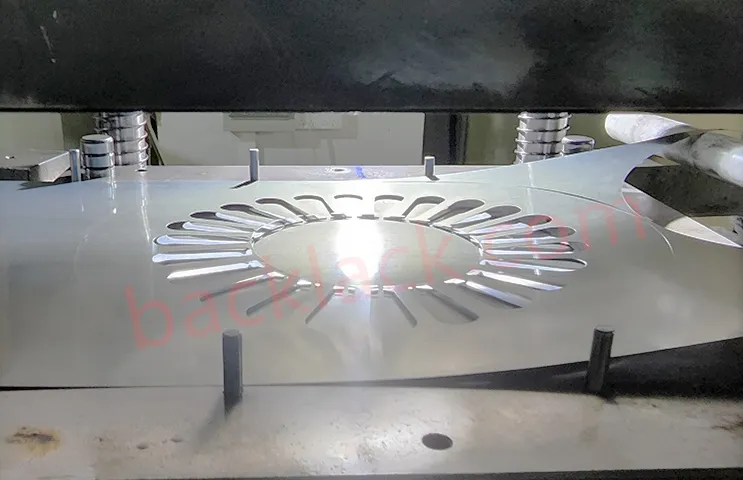
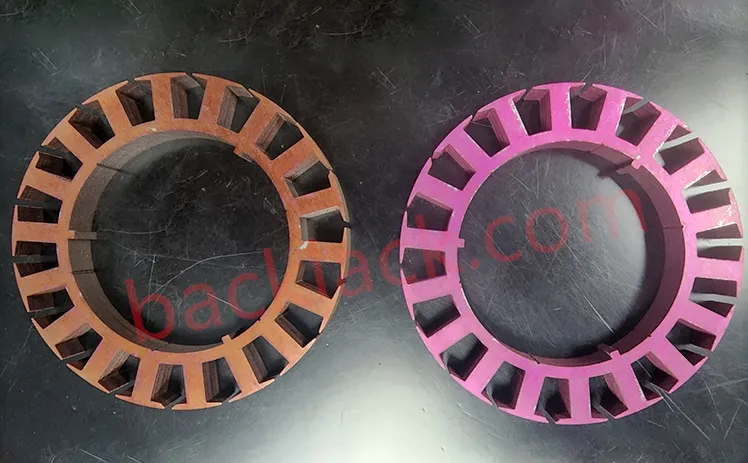
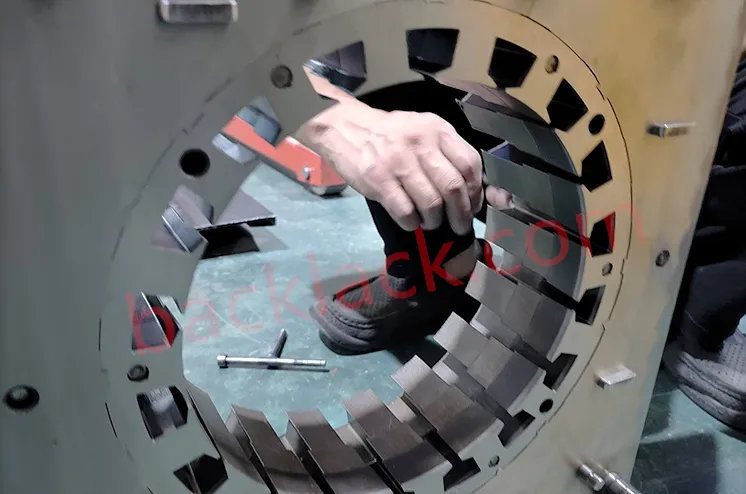
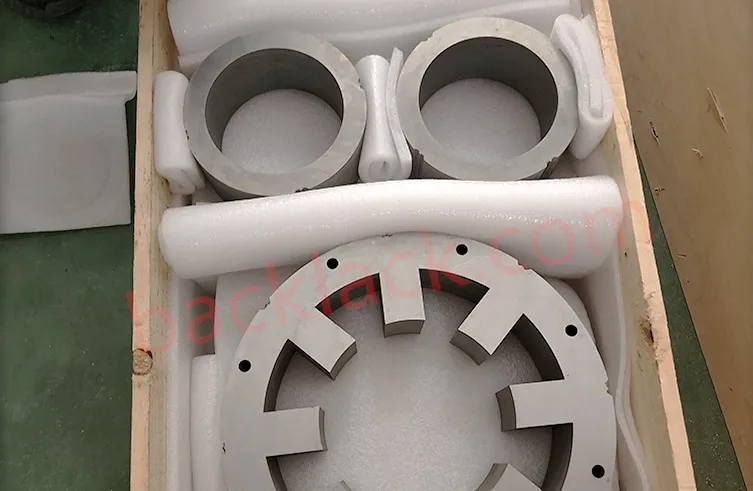
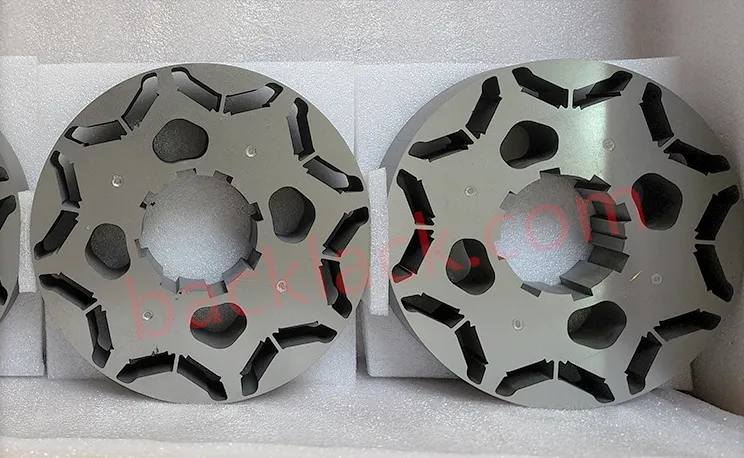
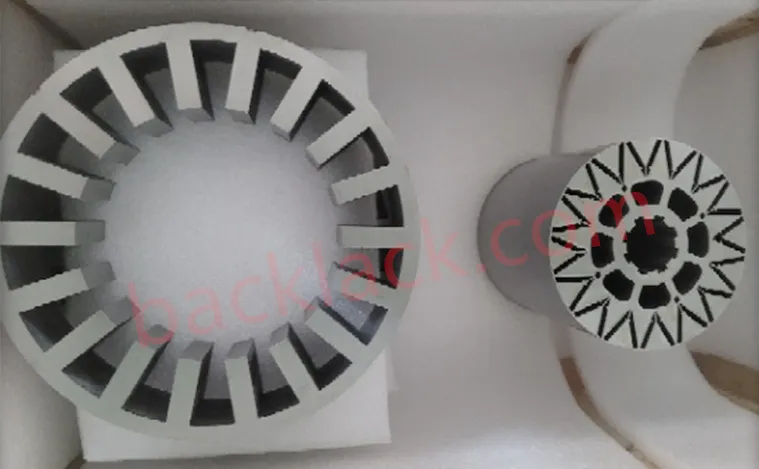
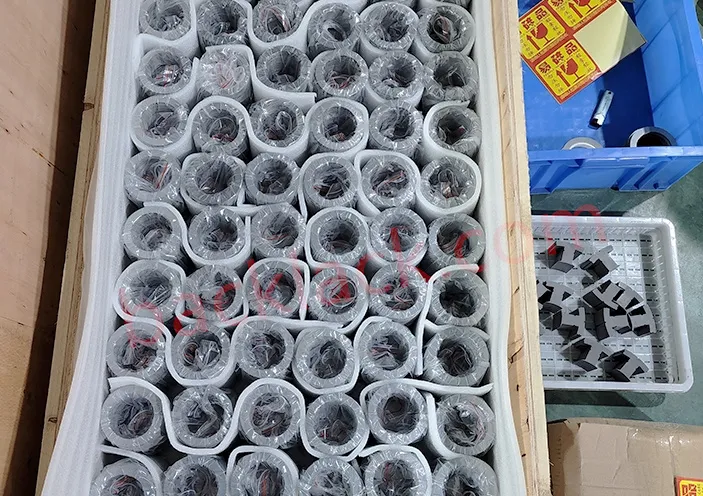
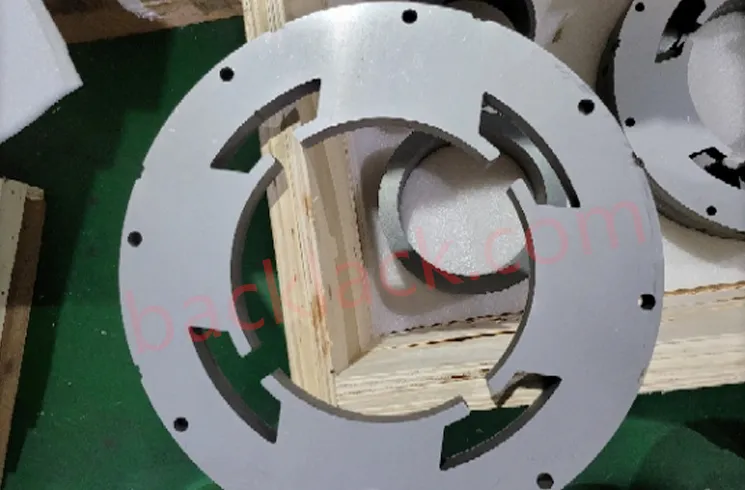
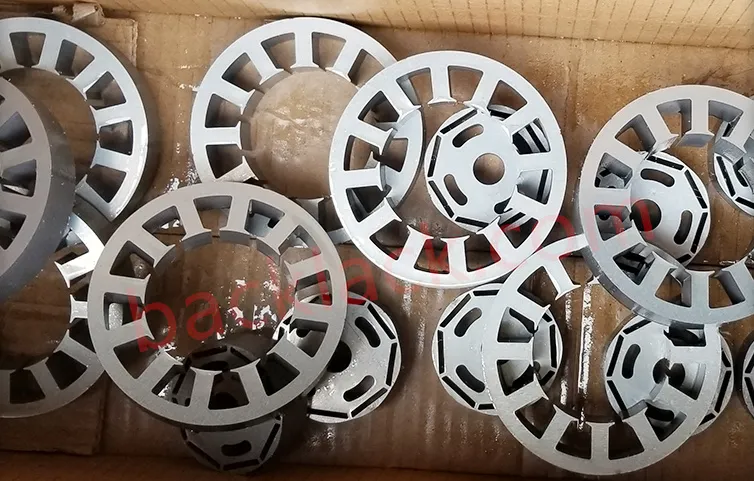
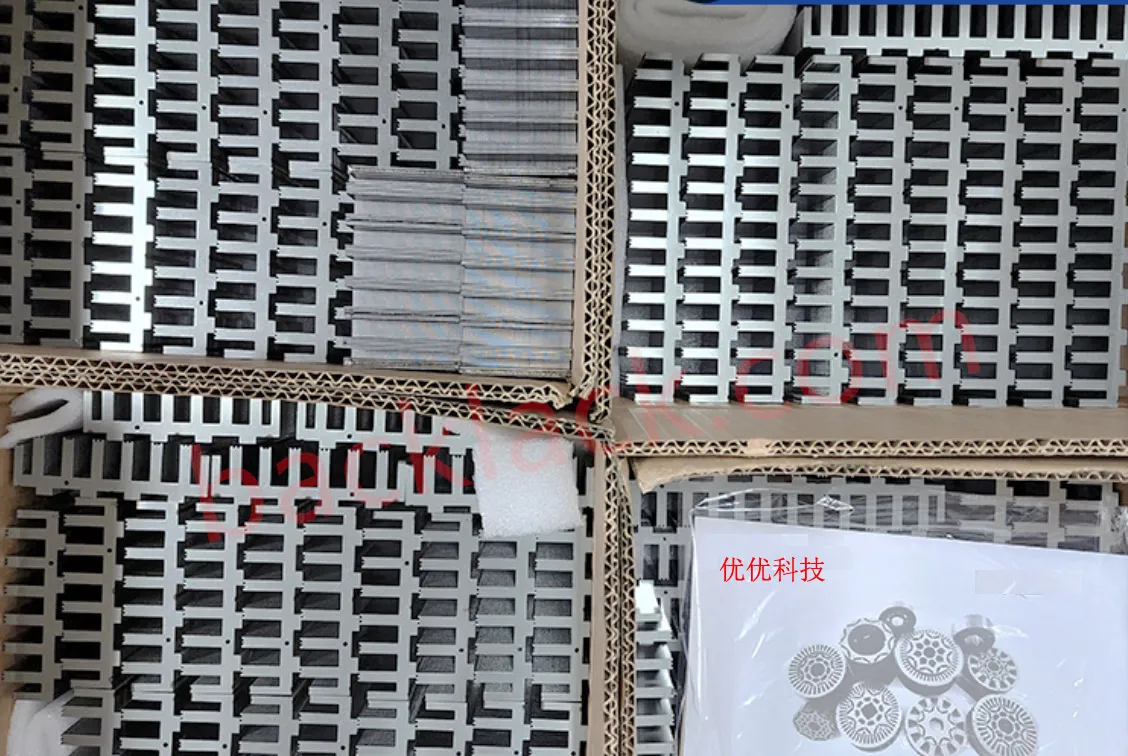



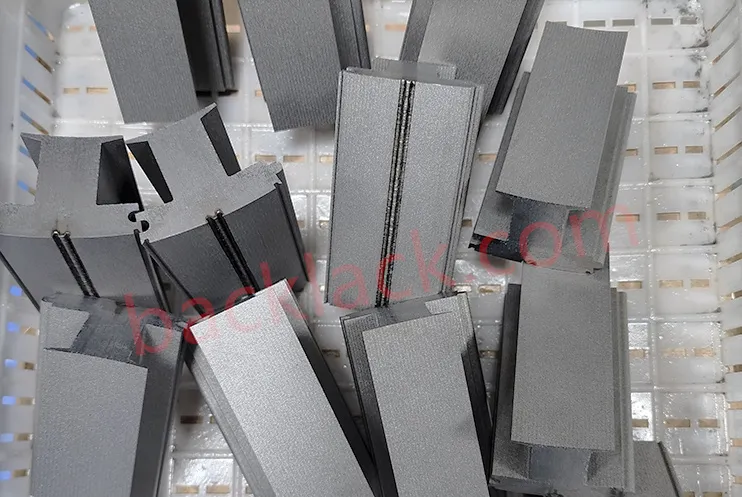

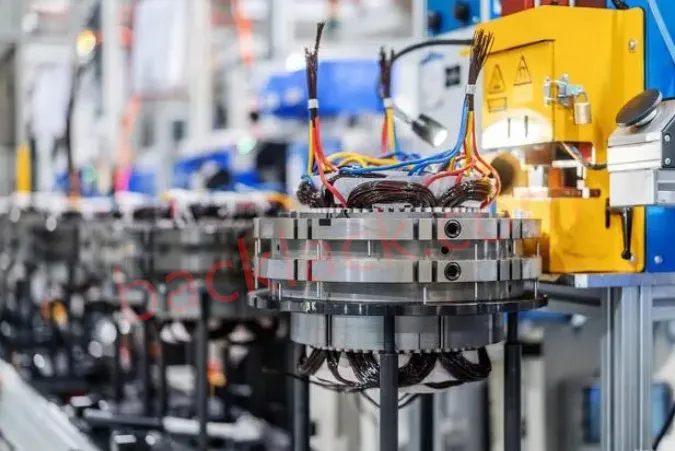












3. On-Site Audit Checklist: What to Verify in Person
On-site audits are the most reliable way to evaluate a manufacturer. Based on our experience, focus on these key points during your visit:
- Check production equipment advanced level: CNC stamping machines, laser welding equipment, and precision inspection instruments (CMM, laser interferometer) should be up-to-date (within 5 years).
- Observe 5S management: A clean, organized production site reflects strict quality control. Messy workshops often lead to cross-contamination and defective products.
- Review batch records: Ask for past production logs, QC reports, and customer feedback to verify consistency.
- Test sample cores on-site: Bring your own testing tools to verify dimensional accuracy, insulation resistance, and magnetic properties—don’t rely solely on the manufacturer’s data.
Final Takeaway: Precision Is the Core of Cooperation
As a motor core processing factory, we’ve learned that high-performance stator cores are the result of strict material control, advanced processing technology, and full-process QC. When choosing a manufacturer, don’t be misled by low prices or fancy marketing—focus on micro-precision and practical capabilities.
A reliable stator core manufacturer is not just a supplier, but a partner that helps you improve motor efficiency and competitiveness. By following the guidelines above, you can select a partner that meets your needs and avoids costly quality issues.
Looking for a manufacturing partner?
Whether you’re designing a new motor for industrial automation, upgrading an EV powertrain, or building precision medical equipment, we have the expertise to deliver laminations that elevate your product’s performance.
Request a Technical ConsultationContact us today to share your motor lamination requirements—we’ll provide a free quote and design consultation to help you find the perfect solution.
About Youyou Technology
Youyou Technology Co., Ltd. specializes in the manufacture of Self-bonding precision cores made of various soft magnetic materials, including Self-bonding silicon steel, ultra-thin silicon steel, and Self-bonding specialty soft magnetic alloys. We utilize advanced manufacturing processes for precision magnetic components, providing advanced solutions for soft magnetic cores used in key power components such as high-performance motors, high-speed motors, medium-frequency transformers, and reactors.
The company Self-bonding precision core products currently include a range of silicon steel cores with strip thicknesses of 0.05mm(ST-050), 0.1mm(10JNEX900/ST-100), 0.15mm, 0.2mm(20JNEH1200/20HX1200/ B20AV1200/20CS1200HF), and 0.35mm(35JNE210/35JNE230/ B35A250-Z/35CS230HF), as well as specialty soft magnetic alloy cores including VACODUR 49 and 1J22 and 1J50.