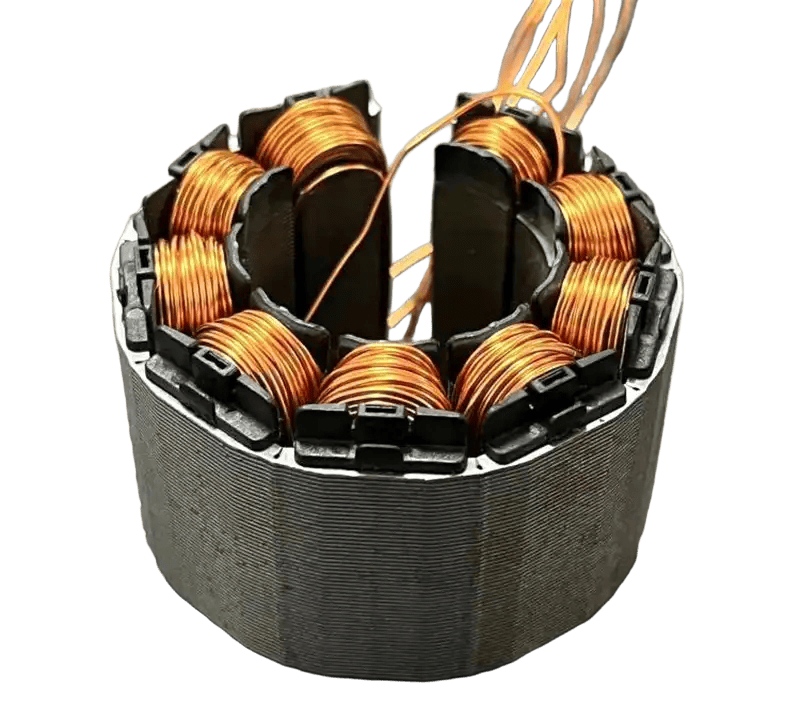
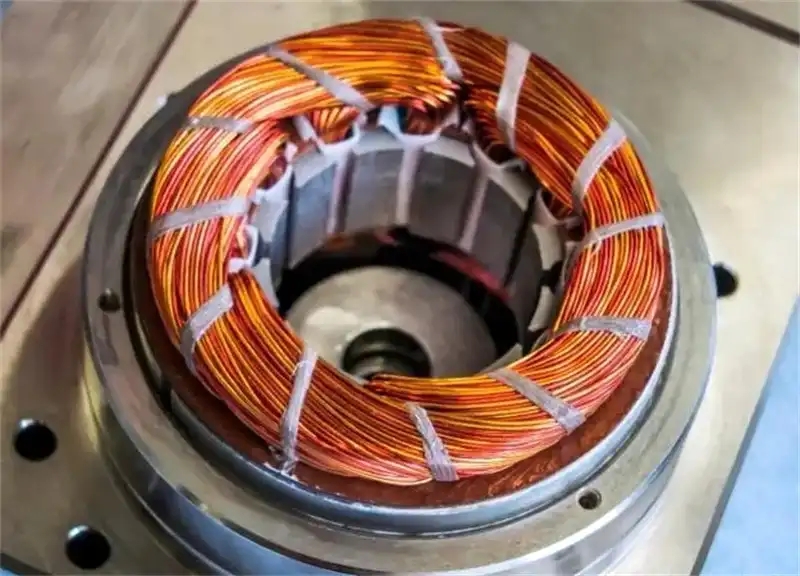
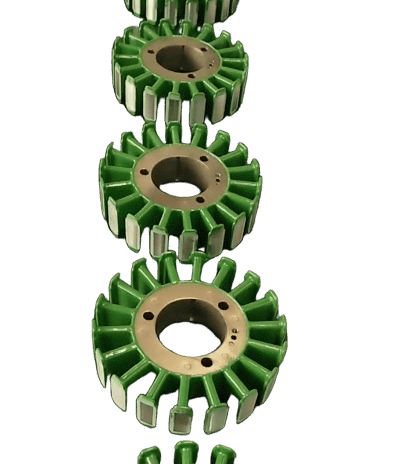
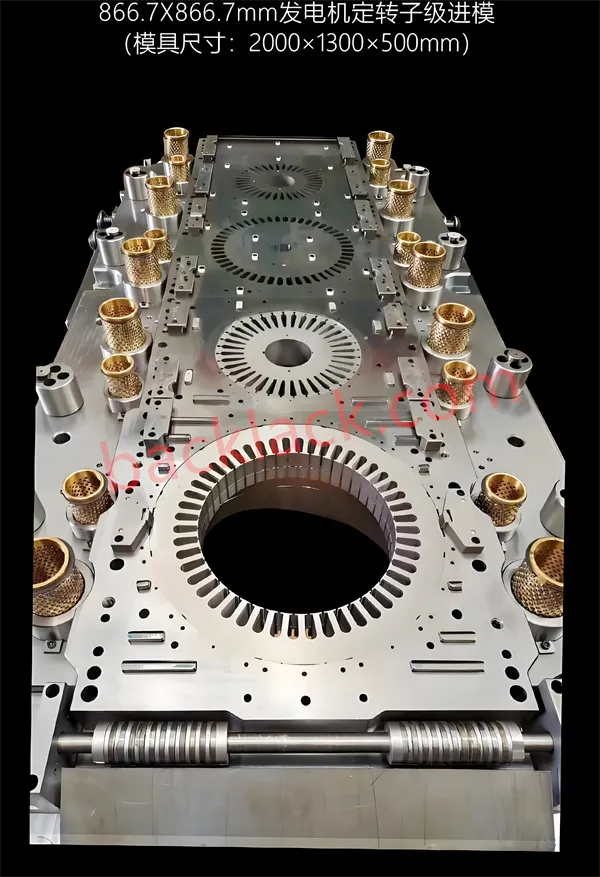
Single punch die vs. continuous die: "Precision defense battle" for motor cores
Thnology completely subverts traditional processes by coating special adhesives on the surface of silicon steel sheets, and forming seamless integral cores after lamination and curing.Let me ask a question first: Why do new energy vehicle companies' 800V high-voltage motors and industrial robots' high-power servo motors begin to abandon continuous dies and use single punch high-precision dies instead?
The answer lies in the underlying logic of "single punching":
|
Although the continuous die (progressive die) is suitable for mass production (such as ordinary motor core), it is completed through "multi-station continuous feeding + multiple stamping". Every time it passes a station, the silicon steel sheet will be "pulled" by the feeder once, and cumulative errors are inevitable - for example, the blanking gap offset is 0.005mm. After 5 stations, the total error may be magnified to 0.025mm, which directly leads to the stacking coefficient out of tolerance. |
|
Even more fatal is the thin-walled special-shaped structure: when the core needs to be made into a 0.3-0.5mm thin-walled groove, bevel or stepped special shape, the "pulling force" of continuous stamping will cause the silicon steel sheet to deform slightly (such as warping) during the blanking process, and the punched shape does not match the design drawing at all. |
|
The single punch die is "done at one time": after the silicon steel sheet is placed, all the punches in the die (may be 10, 15 or even more) act at the same time, completing all processes such as blanking, rib pressing, and notching at one time. There is no pulling from multiple feedings, no cumulative errors from multiple workstations, and the dimensional accuracy of thin-walled special-shaped structures can be directly controlled within ±0.01mm (1/7 of the diameter of a hair), and the burrs are ≤0.005mm (3μm) - this is the "micron-level precision" that high-end motors want. |

TechnicalThe "difficulty" of single punch high-precision molds: thin-walled special-shaped + single-shot molding, each step requires hard-core technology
But single punch molds are by no means "enhanced versions of ordinary molds". To meet the requirements of "single punching" and "high precision and complexity" at the same time, mold manufacturers must tackle three "hard bones":
Structural design: Multi-process integration, as precise as "building blocks"
The core of the single punch die is "multi-process integration" - for example, if you want to punch a fan-shaped iron core with ventilation holes, reinforcing ribs and special-shaped grooves, the mold needs to be arranged at the same time:
The position, angle and pressure of these punches must be accurately calculated: the punch for punching ventilation holes cannot touch the special-shaped grooves next to it, the punch for pressing ribs cannot crack the silicon steel sheet at the thin wall, and the combined force of all blanking forces must be balanced to avoid mold deformation.
A leading electric motor factory once asked us to develop a "single punch die for stepped special-shaped iron core". The punch design alone was revised 8 times - because a slight deviation in the punching angle at the thin wall (0.3mm) would cause excessive burrs on the edge; if the punch sequence was wrong by 0.1mm, it would cause "misalignment" when stacking.
Processing equipment: micron-level precision relies on the hard power of "industrial mother machine"
Ordinary processing equipment is not enough to make such a mold. The head mold factory must be equipped with:
Process verification: simulation + mold trial, "nip the risk in the bud"
Once a single punch mold has a problem, the loss is several times that of a continuous mold - because it is "one-time molding", and a failed mold trial may directly scrap it. Therefore, professional mold manufacturers will do two things:
A customer once compared two mold factories: Factory A directly tried the mold 3 times and spent 150,000; Factory B first did 10 simulation optimizations, and the mold trial was successful once, saving 100,000, and the mass production yield was directly increased from 70% to 98%.
|
Energy efficiency revolution |
The self-adhesive structure eliminates the gap between the laminations, reduces eddy current loss by 30%-40%, and reduces iron loss to less than 0.20W/kg. Tight lamination improves thermal conductivity, improves heat dissipation efficiency by 30%, and helps the motor to operate continuously at high load. |
|
NVH performance breakthrough |
The bonding strength reaches 5N/mm² (10 times that of traditional welding), the vibration amplitude is reduced by 60%, and the noise is controlled below 35dB. |
|
Process simplification and cost optimization |
Eliminate welding/riveting processes, shorten production cycle by 40%, and reduce labor costs by 50%. Integrated molding reduces material waste and increases material utilization to more than 98%. |
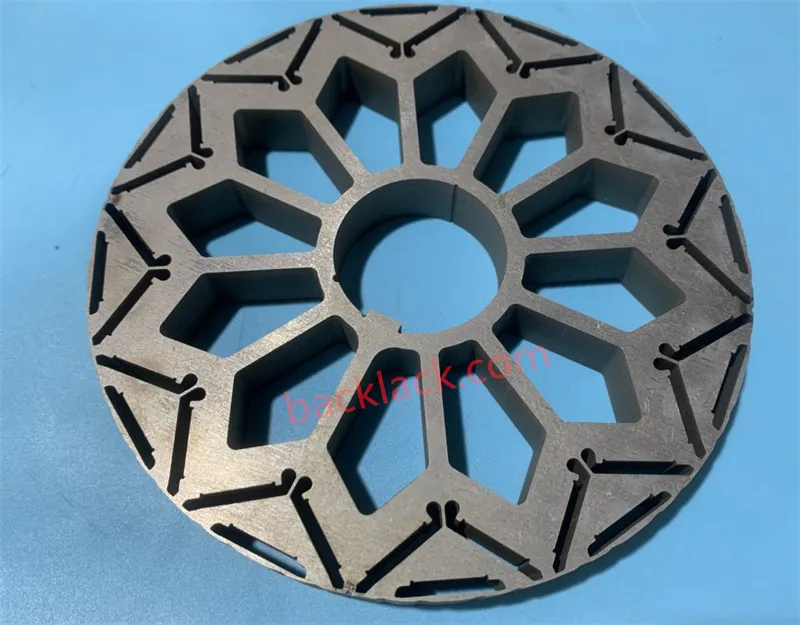

Global application scenarios: practical cases from laboratory to mass production
|
New energy vehicle drive motor |
Tesla Model S Plaid: uses 0.20mm self-adhesive silicon steel laminations, with a rotation speed exceeding 20,000rpm and a power density of 5kW/kg. BYD e-Platform 3.0: Optimizes magnetic flux distribution through the skew slot stacking process to achieve 97.5% working efficiency. |
|
Industrial servo motor |
ABB IRB 6700: uses PPS injection-molded self-adhesive core, which is 40% smaller in size and has a protection level of IP67. |
|
Aerospace field |
GE Aviation LEAP engine: Amorphous alloy self-adhesive core achieves high temperature operation of 200℃ and reduces weight by 30%. |

Future trends: technology iteration and industrial upgrading
Material innovation
Intelligent production line
Green manufacturing
Conclusion
Self-adhesive silicon steel technology - the "hidden champion" of the motor industry
From precision proofing in the laboratory to large-scale application in global production lines, self-adhesive silicon steel lamination technology is reshaping the motor manufacturing landscape with its core advantages of high efficiency, intelligence and environmental protection. With the continuous breakthroughs in materials science and automation technology, this technology will become the "gold standard" in the field of high-end motors, injecting strong momentum into the global Industry 4.0.